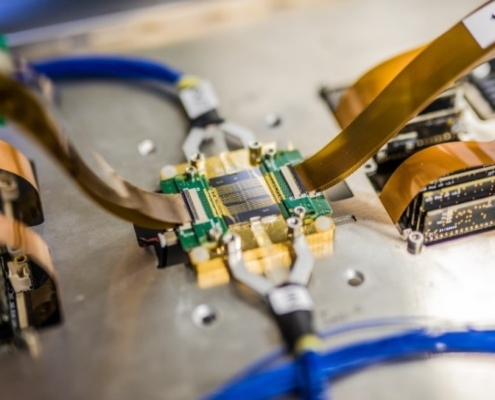
Figure 1: Photonic biosensor chips with integrated light sources on printed circuit boards.
How to build a photonic biosensing diagnostics chip using vertical integration
This week, diagnostics company Surfix BV along with LioniX International and a consortium of Dutch partners announced an €8.5 investment for photonic biosensor development for covid-19 detection and early cancer diagnostics.
LioniX International play a key role in the partnership, which also includes Qurin Diagnostics BV, industry accelerator PhotonDelta and the East Netherlands Development Agency, Oost NL. Using vertically integrated expertise we have developed a technology platform that speaks to the pressing needs of the biosensing market.
But what exactly are those needs? And how does LioniX International’s approach to product development serve innovation in this cutting edge application? In this article we examine the drivers for biosensing innovation, the benefits of photonic biosensing and the unique mix of expertise LioniX International is contributing to its development.
The case for sensitive point of need testing
Biosensors have the power to save lives through early and accurate diagnosis and effective treatment monitoring. Similarly, in veterinary, agriculture, feed and food production applications, biosensing can secure food safety and security, protect stocks and ensure animal welfare.
An effective test must provide accurate information and do so within a relevant timeframe or risk unacceptable consequences. On the other hand, testing speed is also paramount. In the diagnosis of sepsis – a leading cause of death in emergency wards – a delay of hours can severely increase the likelihood of death.
Meeting both the sensitivity and speed criteria with the same test is tricky. The most sensitive tests rely on central laboratories that can be far from the point of need. Moreover, tests that require specialist sample preparation increase turnaround time, rely on trained staff and introduce more possibilities for sample degradation.
Conversely, common point-of-need tests can lack the sensitivity and reliability required for certain applications. A greater issue is that they are fundamentally incapable of testing for a specific subset of biological markers. The technology for antibody or hormone-based lateral flow tests for example (such as the Covid-19 antibody test or home pregnancy test) will never be suitable for tests that look for specific DNA strands or for particularly low concentrations of biomolecules.
Photonic chip biosensing platforms promise not only sensitivity and speed but the flexibility to be configured to detect different analytes for applications from Covid-19 testing to water quality monitoring.
Biosensing basics
Biosensors detect particular biological compounds (or analytes) in a sample. To do this a biosensor combines two parts. The first, a biochemical component, is chosen for its ability to bind with the target analyte. The second is component that can detect and transmit information about the miniscule physical changes that result from this binding.
In photonic chip biosensing, the biochemical component is applied to the surface of a waveguide (think microscopic glass fibre fabricated on a chip) carrying a light signal. In this case, the binding of an analyte changes the way light travels through the waveguide, altering the light signal in way that can be read out by an instrument. Different components operate on different principles. Some detect changes in the absorption of light, others detect changes in the refractive index of the sensor material resulting from analyte binding.
A 100X increase in chip sensitivity for photonic biosensors
In its collaboration with Surfix BV and Qurin Diagnostics LioniX International has developed the most sensitive chip-based photonic biosensing component that is up to 100 times more sensitive than the state of the art. The technology uses refractive index sensing based on a building block known as an asymmetric Mach Zehnder Interferometer (or aMZI).
The particular strength of such aMZIs building blocks for biosensing is that their sensitivity is partly a function of their dimensions. Therefore, with careful photonic engineering, LioniX International have maximised the component sensitivity in a way is not possible with other chip-based components.
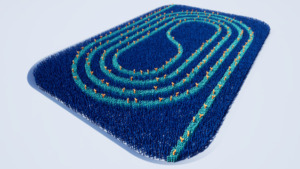
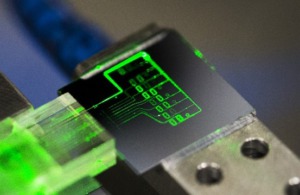
Figure 3 (left): Close up of biochip surface showing the coiled waveguides individual aMZIs transducers. Figure 4 (right): The functionalised surface of the aMZI transducer with biorecognition agents applied on the waveguide surface. Image courtesy of Surfix BV.
Multiplexing is easy with photonic biosensors
The ease with which photonic transducers can be duplicated as sensor building blocks makes them particularly suited for an important biosensing technique called multiplexing. Multiplexing makes for more powerful diagnostic or prognostic testing by simultaneously targeting more than one specific analyte in a sample.
In a multiplexed photonic chip biosensor, any number of generic transducers can be functionalized with a different biochemical compounds, with no fundamental limitation to the compounds that can be used.
From design to device
To develop a technology platform that meets the very specific needs of the biosensing market, LioniX International have drawn on broad expertise from beyond photonics. This has required two approaches to knowledge integration: vertical integration of internal capabilities and horizontal integration of specialist partner expertise.
Vertical integration is the lifeblood of our development process. For the photonic biosensing platform developed for Surfix, we combined expertise in photonics with electronics, fluidics and instrument design. This approach enabled us to develop modules that help Surfix directly address market needs – usability, test reliability robustness and volume manufacturability. Vitally for a commercial product, this approach also ensures that modules are built with a view to volume scalability.
Our partnership with Surfix and Qurin also brought external expertise, vital for two reasons. Firstly, innovation at the forefront of a field relies on access to highly specialised knowledge. The expertise and intellectual property required from different domains like biochemistry, nanotechnology and photonics would be very nearly impossible for a single company to accumulate on its own.
Secondly, close collaboration is vital if LioniX International is to continually develop its understanding of how core capabilities can be applied to new challenges. For example, in collaborating on biochemical surface coatings for photonic chip biosensors, we have come to understand the parameters that limit this technology. By doing so we have been able to develop complimentary electronics fluidics, sample preparation and instrumentation solutions that would have not been possible otherwise. This not only benefits our biosensing partnership, but adds to the body of expertise we can rely on to support other customers bringing technology to market.
R&D for effective product development
To offer value to customers through vertically integrated product development, we need to ensure we can bring serious expertise to the table. The source of this expertise lies not only in product development experience, but also in our own research and development projects.
One such recent project, the EU-funded BioCDX, provided foundational knowledge for photonic biosensor cartridge development. In addition to novel photonic aspects of the sensor, the cartridge design included integrated fluidic syringes for liquid handling and sample preparation and integrated low-cost light sources on the biosensor chip for easy interfacing with a desktop reader.


Figure 5: A low cost injection moulded cartridge (left) with aMZI biosensor chip. The cartridge features integrated microfluidic interfaces (mechanical syringes), blood sample preparation and light source integrated on the biosensor chip. These features make for simple interfacing with a desktop reader instrument (right). Images courtesy of CSEM/BioCDX.
Summary
Integrated photonics is playing a vital role in exciting developments in biosensing. The combination of sensitivity, testing speed and compatibility with a range of target molecules make photonic biosensors attractive in a wide range of medical and non-medical applications.
Despite pressing needs and compelling applications, the use case for biosensors is complex. To develop a cost-effective solution that can outperform existing technology, LioniX International have had to capture expertise that has both high degrees of breadth and specialism. Both are a core aspect of how we do business.
Vertical integration provides the means to develop not just photonic chips, but whole technology solutions. These solutions come in the form of assembled modules incorporating photonics, fluidics and electronics.
Whilst vertical integration leverages internal expertise, partnerships drive the necessary understanding of application required to co-develop cutting edge products.
Whether in biosensing or beyond, this approach to innovation and product development has proven impact. Through vertical integration from design to device, LioniX International is bringing the power of integrated photonics to a range of demanding applications.
References
Chatzipetrou, M.; Gounaridis, L.; Tsekenis, G.; Dimadi, M.; Vestering-Stenger, R.; F. Schreuder, E.; Trilling, A.; Besselink, G.; Scheres, L.; van der Meer, A.; Lindhout, E.; G. Heideman, R.; Leeuwis, H.; Graf, S.; Volden, T.; Ningler, M.; Kouloumentas, C.; Strehle, C.; Revol, V.; Klinakis, A.; Avramopoulos, H.; Zergioti, I. A Miniature Bio-Photonics Companion Diagnostics Platform for Reliable Cancer Treatment Monitoring in Blood Fluids. Sensors2021, 21, 2230. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21062230
Source: Lionix International news